Topic
Surveyors from BUT save cultural monuments
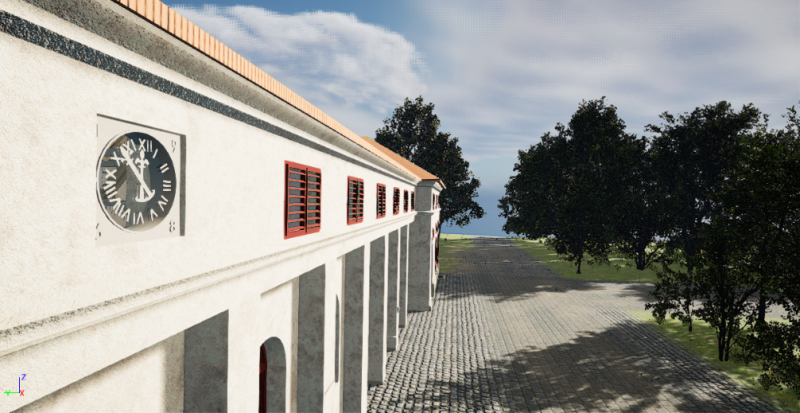

Precise measurements, laser scanning, information modeling and visualization using the tools of the game development environment will make it possible to gently reconstruct the heritage-protected Maxmilián's yard in the Podzámecká garden in Kroměříž. Modern methods solve the problem known to all builders with insufficient or completely missing documentation of historical buildings.
There are more than forty thousand immovable cultural monuments in the Czech Republic, over seven hundred of which are on the endangered list. Researching old buildings is an important part of learning about the life and thinking of our ancestors as well as the maturity of society. Digitization and advanced technologies make the work of preservationists easier and faster.
Digital modeling
Creating documentation of heritage-protected buildings in a comprehensive digital form is an important step in the process of saving cultural heritage and enables the preservation of as much information as possible about immovable cultural monuments for future generations. The creation of a building information model (BIM for short) begins with precise data collection. BIM then serves as a basis for drawing up project documentation for individual construction professions during the reconstruction of the building.
The documentation of monuments is complicated not only by the lack of original drawings, but also by the characteristic elements of specific historical styles, which are not easy to document in a standard way. Ancient buildings are characterized by specific constructions, such as vaulted ceilings, non-vertical walls in the sense of e.g. tapering thickness of masonry with increasing floors and generally a less fine final treatment of surfaces, when, for example, it is not possible to talk about the flatness of clay floors or stone masonry with regard to current standards.
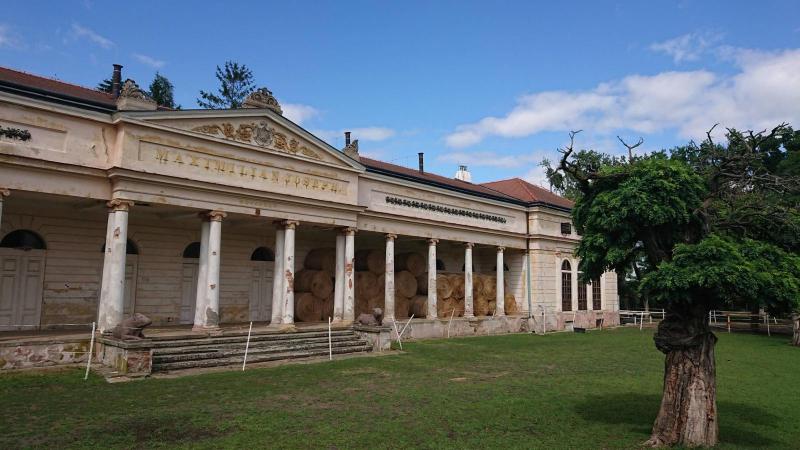

The research team used a so-called total station, which simultaneously measures angles, lengths and elevations, satellite equipment for determining the spatial position of points, and a laser scanner when surveying Maxmilián's courtyard. Using a point cloud, they then generated a spatial model that describes the geometric shape and layout of the building in question (walls, floors, windows, doors, stairs, roof, roof, etc.) as well as individual elements of the building's technical equipment (sanitary equipment, lighting, heating, fire extinguishers, etc.) .).
Gaming for designers
Digital modeling of old buildings requires the enrichment of the non-geometric properties of the elements that make up the model. It is also necessary to take into account the often unique details of complicated shapes and surfaces. Professionals therefore have to create these special elements for complex BIM, because none of the commonly used software includes them in their libraries.
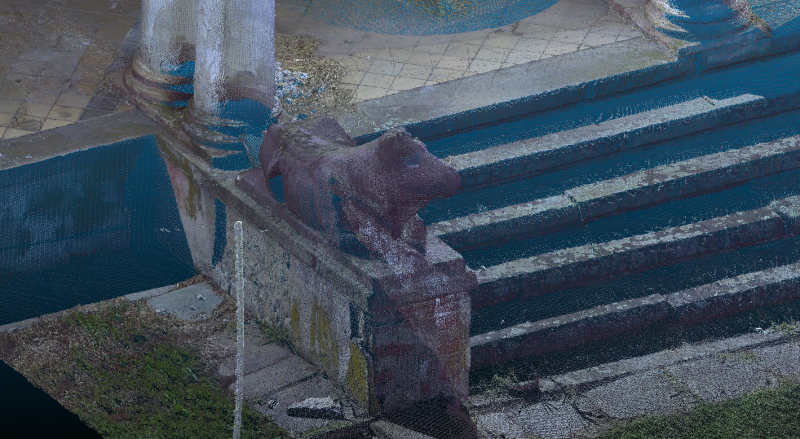
"Characteristic decorative elements, which are also very non-standard, are the statues of cows on the building. In order to record them accurately and preserve their historical value, we decided to create a detailed mesh model (triangular network) for each sculpture from the cloud of points," points out one of the biggest pitfalls in modeling Kuruc.
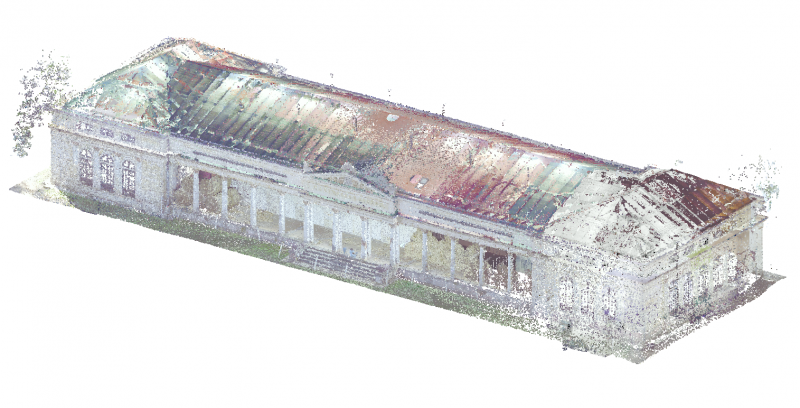
Surveyors from BUT used the Unreal Engine environment for the final modeling and BIM correctness check. Game tools allow a higher level of interaction with the digital world (in our case, a BIM model), namely more realistic visualization compared to technical CAD/BIM applications, e.g. flying over or passing through a building, displaying information about elements, adding realistic materials or artificial lighting. The output from the game development environment does not have to be only visualization in the form of images, it can also be a video sequence or a desktop application, or an application for virtual reality glasses. The documentation of the actual execution of the building is followed by a visualization of the model, which highlights the historical value of the Maxmilian Court building. The researchers created a scene with their own BIM model and surroundings, including surfaces and vegetation, as well as realistic materials and defect impressions on the facades and columns, so that the resulting appearance corresponds to the actual condition of the building.
Modern technologies and their rapid development are constantly opening up new possibilities even in fields where it was almost unimaginable before. Experts from the Faculty of Civil Engineering now want to focus on the implementation of data structures according to individual fields, so that the game environment can be used more not only for playing games, but also for the purposes of technical applications.
Maxmiliánův dvůr (now called the Hubertcentrum) forms part of the well-known Podzámecká Garden in Kroměříž. It was built in 1844 and 1845 by Archbishop Maximilian Josef Sommerau-Beckh according to the design of the architect Antonín Arche as a model farm building for the archbishopric's needs. It was a then-modern dairy with a cowshed, but in the sense of an English ornamental farm or a French ferme ornée, where beauty was combined with practicality, aesthetic function with economic function. Over time, the area was expanded to include two pavilions in the corners of the courtyard, which created a court of honor (cour d'honneur) and gave the building a nobler character.
Soil erosion will be prevented by strip crop rotation technology
FCE researchers' timeless natural wastewater is one of the best construction in the region
Sustainable energy projects are not a luxury. They can save and make money
BUT experts address climate challenges, floods, and the future of Czech water
Microplastics in drinking water will increase